When we look at Sheffield, the names of two construction firms – George Longden and Henry Boot – often appear. However, some of our well-known buildings were built by a company that has been erased from history. And perhaps for good reason.
William Bissett was a self-made man. Born in Pilsley, Derbyshire, he came to Sheffield and was apprenticed to Primrose and Company, where he acquired a practical knowledge of plumbing and glazing.
Afterwards, he set up on his own on West Street, adding further trades such as gas-fitting, painting, paperhanging, and general decorating. The success of the business allowed him to take on a partner, John Edwin Elliott, and move to more extensive premises on Devonshire Street, used as offices and showrooms, and workshops at Wilkinson Street, Pinfold Street, and Mary Street.
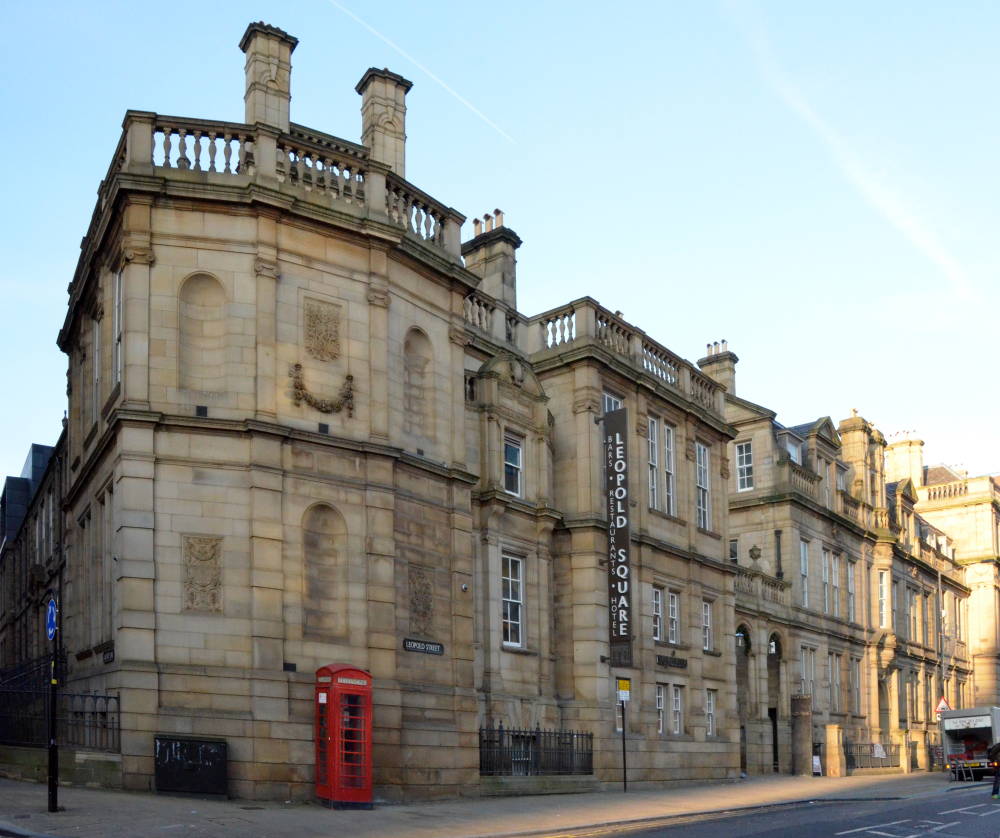
He launched as a general contractor and builder and managed to obtain important contracts in Sheffield and Birmingham. Amongst the earliest of his employers was Mark Firth, who entrusted him to enlarge his residence at Oakbrook, but this work was dwarfed by the magnitude of his public contracts, the most important of which was the Central Schools, School Board offices, and Firth College (now forming Leopold Square and Leopold Hotel).
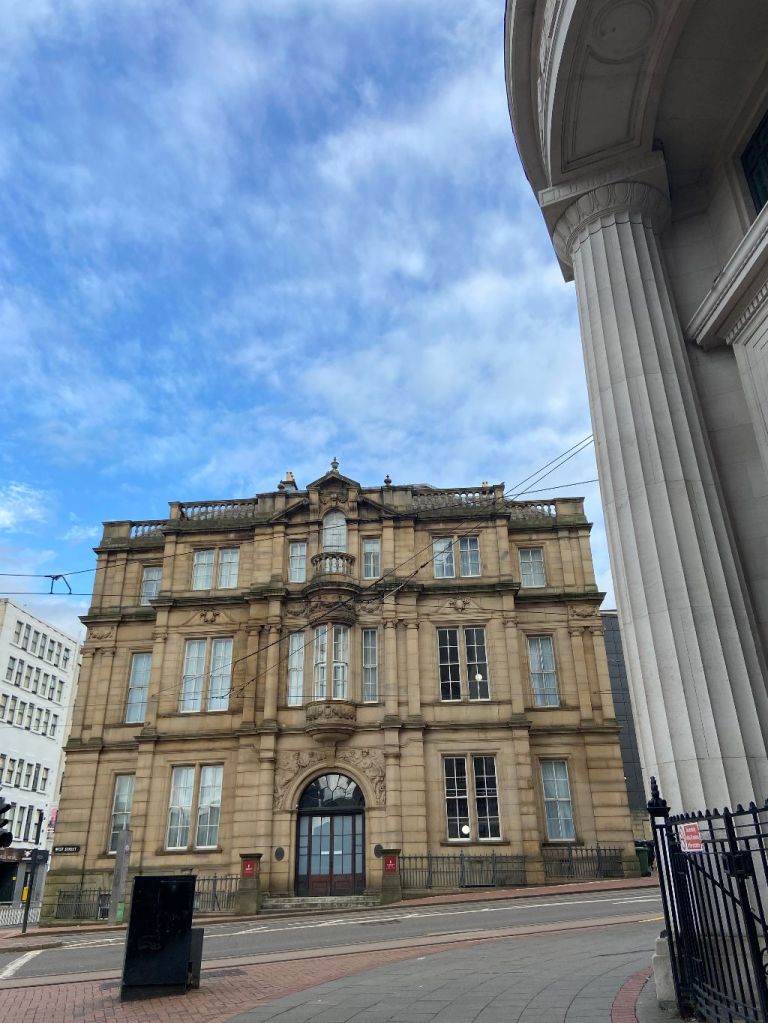

When Sheffield Corporation started its Street Improvement Scheme in the 1870s, Bissett was extensively engaged in the erection of palatial; new business premises on Fargate and Pinstone Street, and himself acquired several valuable sites.
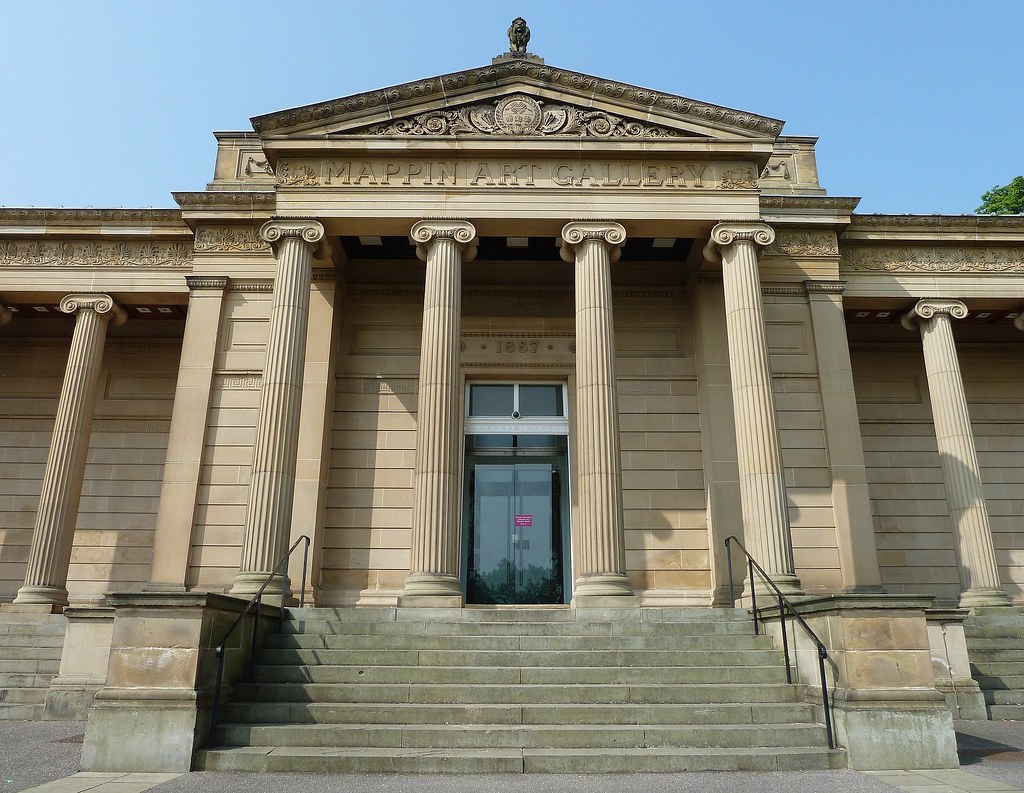
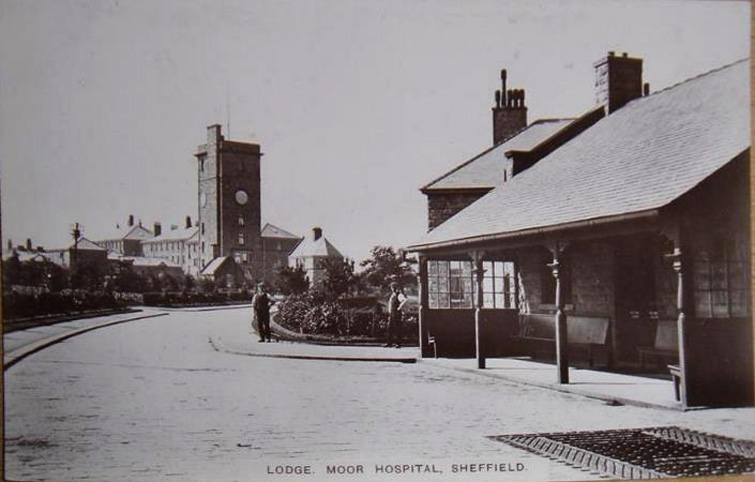
Other building work included Weston Park Museum, Mappin Art Gallery, Cockayne’s department store in Angel Street, and Lodge Moor Hospital.

For some years, Bissett was a member of Sheffield Town Council for the Upper Hallam Ward, serving on the Buildings, General Purposes and Parks, and Highway Committees. Far from me to speculate that the success of his company might have been down to council connections, but these weren’t transparent days. However, he resigned in 1884 to allow his firm to undertake the Sewage Works at Blackburn Meadows.
Unfortunately, Bissett suffered a stroke in 1886, and died at Rock Mount, Ranmoor, in 1888. His partnership long dissolved, the business was split amongst three sons, but hereon, the affairs of William Bissett and Sons unravelled.
In 1889, whilst work was underway to build buildings for the YMCA (Carmel House), on Fargate, a petition was served against his three sons.
“The acts of bankruptcy alleged against the debtors respectively are that William Crellin Bissett and Lawrence Colgrave Bissett, did, on or about the 28th of November, 1889, with intent to defeat or delay their creditors, depart from their dwellings or otherwise absent themselves; and that the said James Francis Bissett did, on the 4th day of December, file in the Sheffield Court a declaration admitting his inability to pay his debts.”
It appeared that some of the contracts did not turn out very successful and the firm had lost considerably by them. A year before, a destructive fire at the Wilkinson Street premises had also caused considerable loss. Stories about the firm’s financial position had circulated for months and everything that could be offered as security, even their interest under their father’s will, had been mortgaged.

But the situation took a grimmer turn.
Apparently, the state of affairs was only known to the brothers in Sheffield, William and Lawrence, while James, in Birmingham, had been kept ignorant. The first he knew about it was when he received a letter from them bearing a Paris postmark and informing him that they had absconded.
James immediately came to Sheffield and found that the firm was in a state of financial ruin. From inquiries he learned that both William and Lawrence had been about the business on the Thursday morning, and that early in the afternoon they had left for London. They travelled to either Dover of Folkstone the same evening and caught a boat to Paris. The assumption was that they had then gone to Spain.
Before they left, they had received a cheque for about £4,000 to which debt they obtained advances. They cashed the cheque, took the proceeds, and with them went the petty cash books and private ledgers. In the end, it was determined that the company owed creditors about £34,439 (about £4.7m today).
James, left to deal with his brothers’ dirty work, and the discovery that they been living way beyond their means, was absolved, and eventually released from bankruptcy.
However, the whereabouts of William and Lawrence remained a mystery and by all accounts never returned to England.
Until that is, a notice headed ‘Bissett v Bissett’ appeared in The Times in 1897, whereby Agnes Amy Bissett filed for divorce against her husband Lawrence, by reason of his adultery and desertion.

On November 28, 1889, Lawrence had told her that he was going to London to see his solicitors about business, but he never returned, and the next she heard from him was through a letter he sent to her father from Paris, in which he said: –
“Will you please, on receipt of this, go to Amy at once. Our affairs have gone wrong, the bank having turned on us, and to save a little money from the wreck, I have left England for a time. I may have done wrong, if I have, God forgive me. I have no time for more, as the train goes.”
In a subsequent letter he wrote:-
“We had a certain overdraft from the bank, and all went well. They have suddenly shown us that they will not continue it, and nothing but bankruptcy, without a chance of saving anything, stared me in the face, so I thought it best, rightly or wrongly, to leave England with what money I could and try my fortune in another land.”
It was subsequently found that he had gone to San Antonio, Texas, and as a bankrupt, the Official Receiver had instructed the Post Office to send all letters to them.
In this way, another letter came to light from a young lady called Amy Sebright. This letter announced to him that she had given birth to a boy called Cyril Laurence Bissett. It transpired that the young lady had been engaged at the Theatre Royal during the pantomime season of 1888-1889, and that she had met Lawrence, and afterwards lived with him ‘maritalement’ at Manchester, Brighton, and elsewhere. When he was leaving England, he had asked her to accompany him, but she had declined to do so
His wife received another letter from him at the end of 1890 asking for her forgiveness, and acknowledging his guilt, but said nothing about returning.
The divorce was granted.
“Here the husband had left his wife with a falsehood on his lips, and there could be no doubt of his intention to desert her after what had transpired as to his relations with the actress from Sheffield.”
We do not know the end outcome for William or Lawrence (investigations for another day). Bad businessmen, rogues, and criminals. Only James came out of the story with his reputation intact. Remember this story the next time you visit Leopold Square or Weston Park Museum.

©2022 David Poole. All Rights Reserved.


